HVAC electrical training is a critical component of becoming a skilled technician in the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning industry. At Iowa Trade School, we recognize the importance of mastering electrical systems for HVAC professionals.
This blog post will explore the essential electrical components, troubleshooting techniques, and advanced skills needed to excel in HVAC electrical work. We’ll also discuss how these skills can lead to exciting career opportunities in this growing field.
Essential HVAC Electrical Components
Understanding the electrical components of HVAC systems forms the foundation for any technician in the field. Several key components work together to regulate temperature, control airflow, and ensure efficient operation.
Thermostats: The Control Center
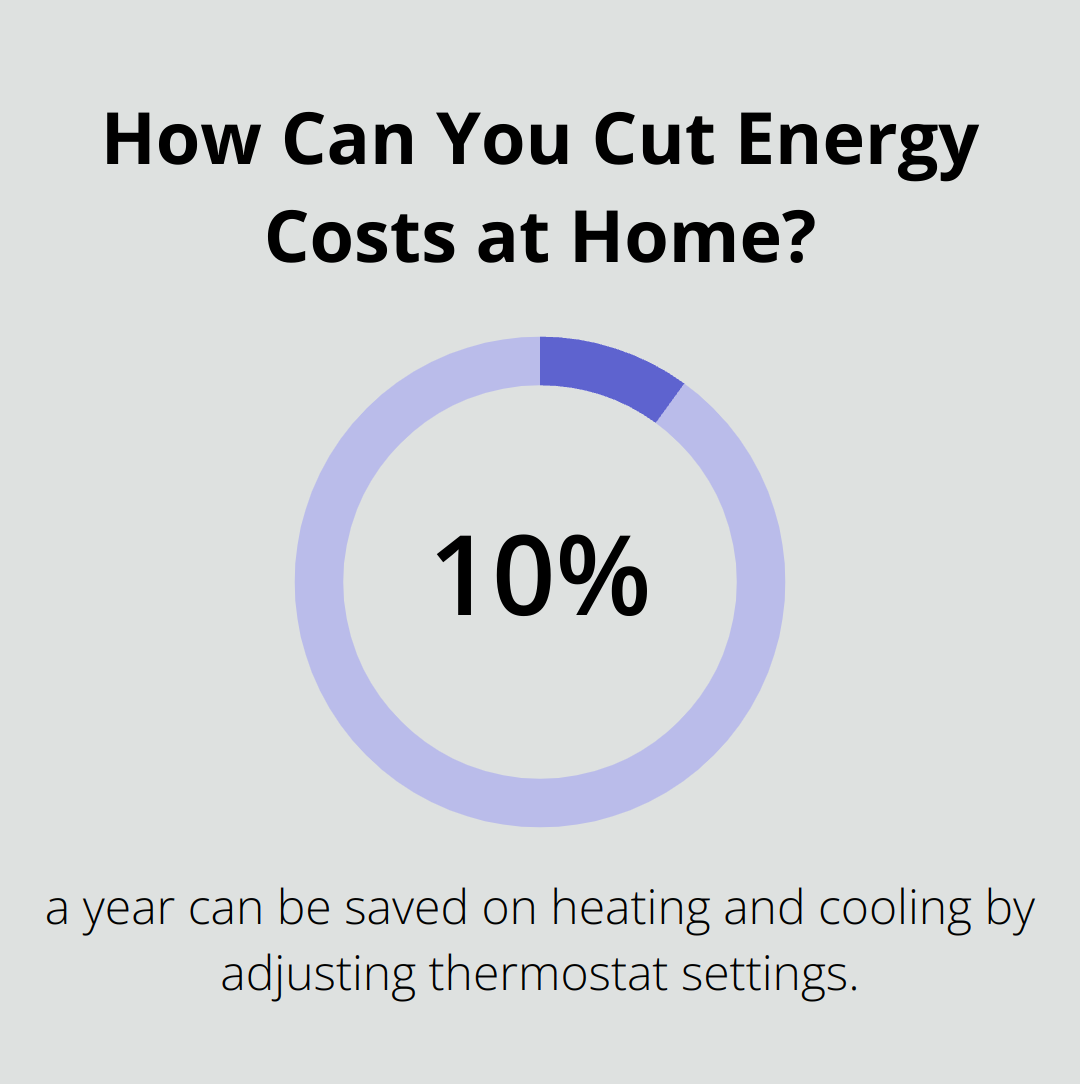
Thermostats act as the control center for HVAC units. They monitor room temperature and signal the system to turn on or off based on preset conditions. Modern programmable and smart thermostats offer advanced features like scheduling and remote access, which can significantly improve energy efficiency. You can save as much as 10% a year on heating and cooling by simply turning your thermostat back 7°-10°F for 8 hours a day from its normal setting.
Capacitors: Motor Power Boosters
Capacitors store electrical energy and provide the extra boost needed to start compressors and fan motors. Two main types exist: start capacitors and run capacitors. Start capacitors provide the initial jolt to get motors running, while run capacitors help maintain motor operation. Regular inspection of capacitors prevents motor burnout.
Contactors: Electrical Flow Controllers
Contactors control the flow of electricity to major components like compressors and fan motors. When the thermostat signals for cooling or heating, the contactor closes its contacts, allowing current to flow. Proper maintenance of contactors prevents issues like arcing or welding of contacts, which can lead to system failure.
Safety and Wiring Considerations
Electrical safety takes precedence when working with HVAC systems. Technicians must always disconnect power before servicing any electrical components. The use of insulated tools and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is mandatory when handling electrical parts. Regular training and adherence to safety protocols prevent accidents and ensure longevity in the HVAC profession.
Proper wiring serves as the backbone of any HVAC electrical system. Incorrect wiring can result in short circuits, system inefficiency, or even fire hazards. Technicians must follow manufacturer specifications and local electrical codes when installing or repairing HVAC systems. The National Electrical Code (NEC) is enforced in all 50 states and serves as the benchmark for safe electrical design, installation, and inspection. Staying updated with these standards is essential for HVAC professionals.
As we move forward, we’ll explore how these components come into play during electrical troubleshooting for HVAC systems, a skill that sets apart exceptional technicians in the field.
Troubleshooting HVAC Electrical Issues
Common Electrical Faults in HVAC Systems
HVAC technicians frequently encounter electrical problems in the field. The Air Conditioning Contractors of America (ACCA) reports that approximately 80% of HVAC service calls involve electrical issues. Technicians often face challenges such as short circuits, open circuits, and ground faults. Faulty capacitors, worn contactors, and malfunctioning thermostats rank among the most prevalent electrical problems in HVAC systems.
Systematic Diagnosis Approach
A structured approach to diagnosing electrical issues includes:
- Verify the complaint: Confirm the customer’s reported problem.
- Perform a visual inspection: Look for obvious signs of damage or wear.
- Conduct voltage tests: Use a multimeter to check for proper voltage at key points.
- Test components: Systematically examine individual components (capacitors, contactors, motors).
- Analyze results: Interpret the findings to determine the root cause.
Essential Tools for Electrical Troubleshooting
Effective diagnosis and repair of HVAC electrical problems require a well-equipped toolbox. A high-quality digital multimeter (such as the Fluke 116 HVAC Multimeter) stands out as the most important tool for its accuracy and HVAC-specific features.

Other essential tools include:
- Clamp meter (for measuring current without breaking the circuit)
- Insulated screwdrivers and wire strippers
- Non-contact voltage tester (for quick safety checks)
- Capacitor tester (for accurately diagnosing capacitor issues)
Proficiency with these tools proves invaluable for developing the confidence and skills needed to tackle real-world HVAC electrical problems.
Safety Protocols in Electrical Troubleshooting
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) identifies electrocution as one of the leading causes of workplace fatalities in the construction industry (which includes HVAC work). Safety protocols must include:
- Disconnecting power before working on electrical components
- Using appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Following lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental power-up
- Never working alone on high-voltage systems
Prioritizing safety and adhering to a systematic troubleshooting approach allows HVAC technicians to efficiently diagnose and resolve electrical issues. This expertise ensures optimal system performance and customer satisfaction. As the field of HVAC technology continues to evolve, technicians must stay updated on advanced electrical skills to remain competitive in the industry.
Mastering Advanced HVAC Electrical Technologies
Variable Frequency Drives: Precision Control
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) have transformed HVAC systems by enabling precise motor speed control. These devices adjust the power frequency supplied to motors, allowing variable speeds instead of simple on/off operation. This capability results in significant energy savings and improved system performance.

Older, inefficient commercial rooftop unit (RTU) air conditioning systems are common and can waste from $1,000 to $3,700 per unit annually, depending on the system. Technicians who excel in VFD installation and maintenance are highly sought after. Required skills include VFD parameter programming, troubleshooting communication issues between VFDs and building automation systems, and optimizing VFD settings for maximum efficiency.
Smart HVAC Systems: The Future of Climate Control
Smart HVAC systems incorporate advanced sensors, wireless connectivity, and machine learning algorithms to optimize comfort and energy use. These systems predict heating and cooling needs based on occupancy patterns, weather forecasts, and other factors.
Various smart technologies for commercial building end uses including HVAC, lighting, and plug loads have been studied in-depth. Technicians must develop skills in networking, data analysis, and IoT (Internet of Things) technologies to effectively install and maintain these systems.
Electrical Upgrades for Energy Efficiency
Upgrading electrical components in existing HVAC systems can lead to substantial energy savings. For example, replacing standard PSC (Permanent Split Capacitor) motors with ECM (Electronically Commutated Motor) can reduce energy consumption by up to 75% in some applications.
Advanced HVAC technicians should familiarize themselves with energy auditing techniques, calculate return on investment for electrical upgrades, and stay informed about the latest energy-efficient technologies. This expertise allows them to provide valuable recommendations to clients who want to reduce energy costs and improve system performance.
Continuous Education and Skill Development
The field of HVAC electrical technology evolves rapidly. Technicians must stay current with these advancements for career growth. Continuous education and hands-on experience with cutting-edge systems are essential for technicians who want to excel in this dynamic industry.
Iowa Trade School offers comprehensive HVAC training programs that cover these advanced electrical technologies. Our courses (which range from 4 to 12 weeks) provide students with the practical skills and knowledge needed to succeed in the evolving HVAC industry.
Final Thoughts
HVAC electrical training equips technicians with essential skills for success in the industry. Professionals who master electrical components, troubleshooting techniques, and advanced technologies position themselves for lucrative career opportunities. The growing focus on sustainable building practices and energy conservation expands the potential for HVAC experts with strong electrical knowledge.
Iowa Trade School prepares students for HVAC electrical work through comprehensive programs. Our courses provide practical skills and knowledge aligned with industry demands, supported by experienced instructors and career services. We offer various financial aid options to make quality HVAC education accessible to aspiring technicians.

The HVAC field continues to evolve, requiring professionals to stay current with electrical technologies and best practices. Choosing a reputable training program and committing to ongoing learning will help technicians thrive in this essential industry. Those with strong electrical skills will lead innovation and efficiency in climate control systems, shaping the future of HVAC.
